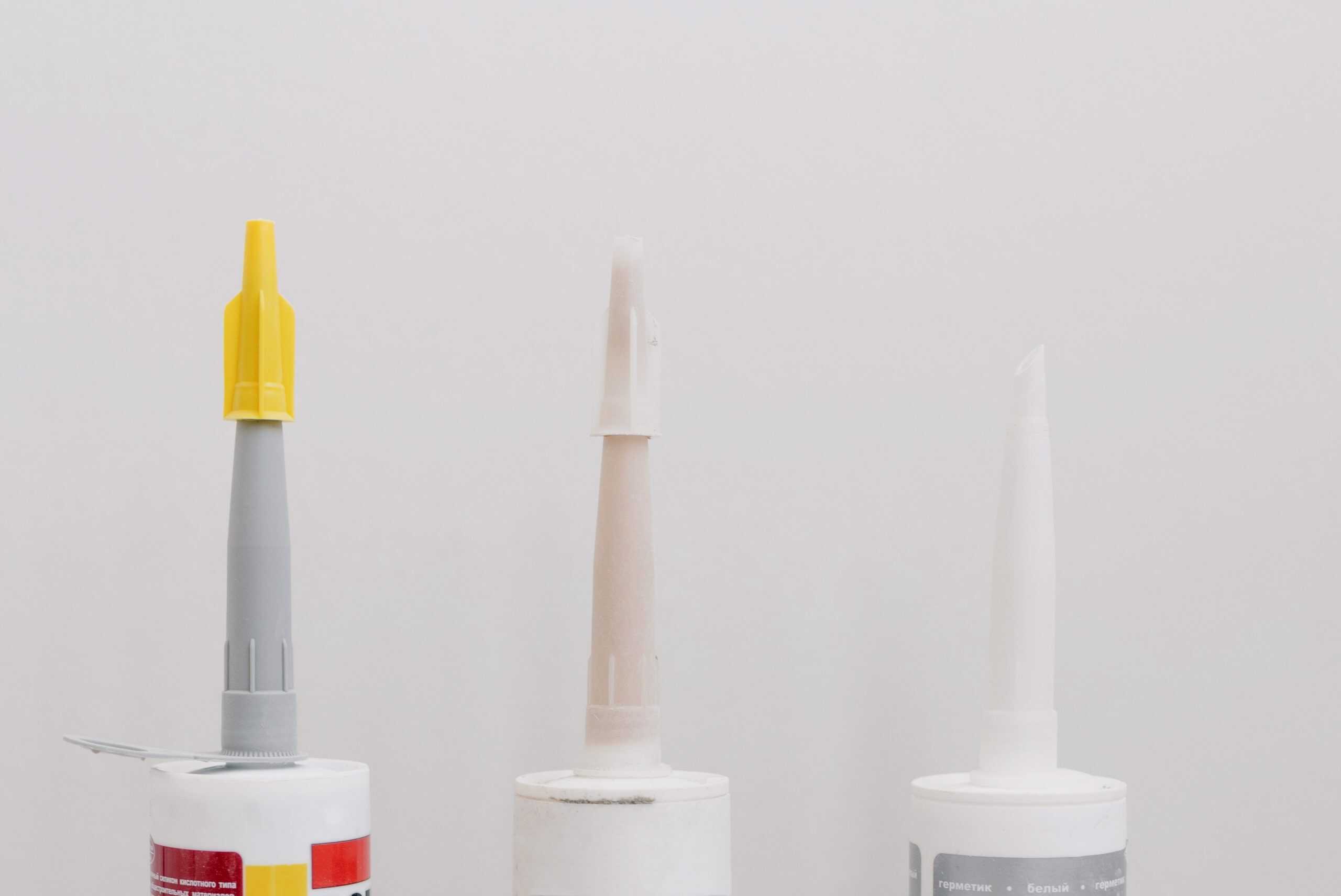
Within the vast realm of manufacturing and construction, where the durability and resilience of materials are paramount, industrial glue takes center stage. Industrial glue manufacturing is a fascinating blend of science and engineering, requiring precision and rigorous quality control. This article will embark on a journey to unveil the intricate world of industrial glue manufacturers, delving into its key elements, methodologies and the profound impact it has on upholding the structural integrity of our world.
Deciphering the Fundamentals
Fundamentally, the production of industrial glue involves developing high-strength adhesive solutions that are painstakingly planned to join a variety of materials, from ceramics and composites to metals and plastics. These adhesives must exhibit attributes including strength, durability and resistance to harmful environmental factors like severe heat, moisture and chemical exposure in order to pass strict performance standards.
Crucial Components of Industrial Glue Production
- Raw Material Selection: The cornerstone of adhesive production lies in the art of selecting the right raw materials. Manufacturers weigh numerous factors, including the types of materials to be bonded and the environmental conditions in which the adhesive will function. Common raw materials encompass polymers, resins, solvents and various additives.
- Formulation and Mixing: The subsequent step involves formulating the adhesive, a process that necessitates the precise blending of raw materials in specific ratios. This step requires an in-depth understanding of polymer chemistry and relies on specialized equipment. The mixing phase is pivotal, ensuring an even distribution of components, a critical factor for adhesive performance.
- Curing Mechanisms: Industrial adhesives typically cure or harden following application. Curing can be facilitated through various mechanisms, such as chemical reactions, heat, or exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. The choice of curing method hinges on the adhesive type and its intended application.
- Quality Control: Rigorous quality control measures are integral throughout the manufacturing journey. This entails testing raw materials for purity and consistency, closely monitoring mixing and formulation processes and subjecting the final adhesive product to rigorous testing to verify its compliance with predefined standards.
Varieties of Industrial Adhesives
Industrial glue manufacturing encompasses a diverse range of adhesive types, each tailor-made for specific applications. Some common adhesive categories include:
- Epoxy Adhesives: Prized for their exceptional strength and longevity, epoxy adhesives are prevalent in aerospace, automotive and construction industries.
- Cyanoacrylate Adhesives: Known as “super glue,” these adhesives cure rapidly and are celebrated for their quick bonding capabilities and versatility.
- Polyurethane Adhesives: Valued for their flexibility and resistance to environmental influences, polyurethane adhesives are well-suited for applications like automotive assembly.
- Acrylic Adhesives: Acrylic adhesives excel in bonding plastics and are commonly used in applications such as signage and automotive manufacturing.
- Structural Adhesives: Engineered for high-load applications, structural adhesives are indispensable in industries where strength and reliability are paramount.
Challenges in the World of Industrial Glue Production
While industrial glue manufacturing is a finely tuned process, it presents its share of challenges:
- Consistency: Ensuring batch-to-batch consistency is imperative in industrial glue manufacturing. Variations in raw materials or process parameters can lead to inconsistencies in adhesive performance.
- Environmental Compliance: Many industrial adhesives contain solvents and chemicals subject to environmental regulations. Manufacturers must adhere to stringent guidelines to minimize their ecological footprint.
- Performance Testing: Guaranteeing that adhesive products meet or exceed performance specifications necessitates comprehensive testing, which can be resource-intensive and time-consuming.
- Customization: Different industries and applications demand adhesive properties tailored to their specific needs. Manufacturers must possess the capability to customize adhesive formulations accordingly.
Conclusion
Industrial glue manufacturing is a captivating blend of science, engineering and quality assurance. The adhesives produced through this intricate process serve as the invisible forces that bind the products and structures shaping our world. As innovation propels the industry forward, you can anticipate the emergence of even more advanced and specialized adhesive solutions. These solutions will cater to the evolving needs of diverse industries while addressing the ever-growing concerns surrounding environmental sustainability. Although the realm of industrial glue manufacturing often operates behind the scenes, its influence is indubitably profound and far-reaching.